
Sleep - What's its role? How does it work?
We're currently professionally translating all content. In the meantime, this article has been translated by Google Translate. Sorry if this isn't 100% relevant.
Sleep - What are its functions?
Sleep is a vital function, essential to:
- good recovery of the body and cell renewal
- to the manufacture of hormones, including growth hormone, which develops muscles, bones, cartilage ...
- strengthening memory and learning ability
To fully understand the functions of sleep, let's go back to the course of a sleep cycle. A sleep cycle lasts approximately 1h30 and is composed of 5 phases:
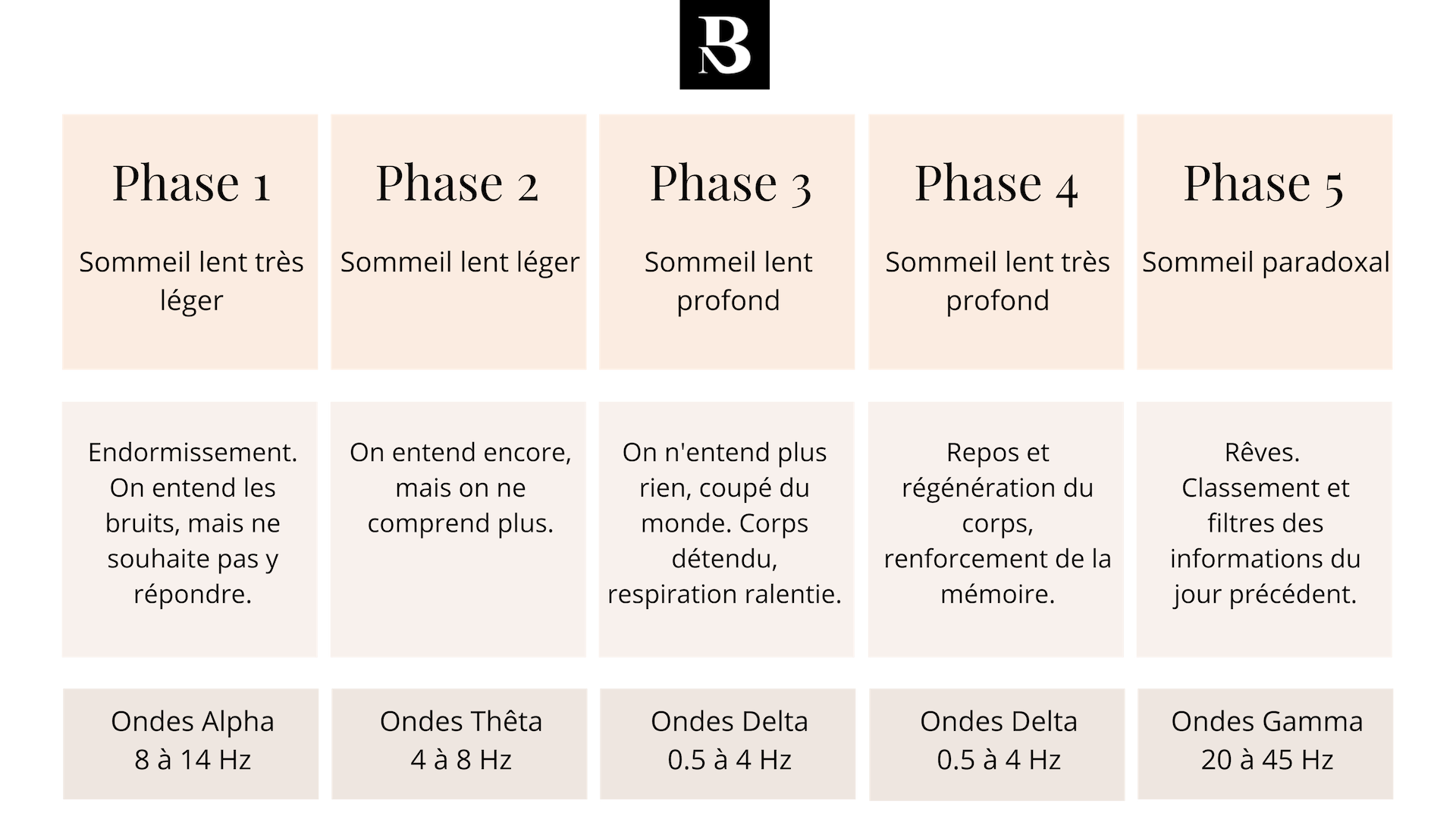
Stage 1
It is very light, slow sleep (sleep phase). It feels like a cloud. The body relaxes, we begin to relax. We hear the sounds, but do not want to answer them.
Brain waves related to sleep in phase 1 are the Alpha waves, which circulate at the rate of 8 to 14 Hz per second. These are the waves of relaxation and regeneration, calm and clear thoughts. When the brain sends you these waves, you feel creative and especially activate acetylcholine.
Stage 2
It is slow slow sleep. We still hear, but we do not understand anymore.
Brain waves related to sleep in phase 2 are Theta waves, which circulate at a rate of 4 to 8 Hz per second. Under the effect of Theta waves, one becomes sleepy (GABA). These are the waves of nervous regeneration, the synchronization of the two cerebral hemispheres, dreams, the subconscious.
Stage 3
This is the stage of deep slow sleep. We do not hear anything, we are cut off from the world. The whole body is relaxed, breathing slows down, body temperature drops.
The waves related to sleep in phase 3 are the Delta waves, which circulate at the speed of 0.5 to 4 Hz per second. When the brain transmits a majority of Delta waves, we sleep deeply (serotonin), without dreams. These are the waves of global regeneration.
Stage 4
It's very deep slow sleep. One sleeps very deeply, it is in this phase that the body really rests, that one best manufactures the growth hormone, thus the systems of defense and regeneration of the organism. The memory gets stronger, it's the beginning of dreams.
The waves related to sleep in phase 4 are also the Delta waves, which circulate at the speed of 0.5 to 4 Hz per second. When the brain transmits a majority of Delta waves, we sleep deeply (serotonin), without dreams. These waves are associated with two anti-aging hormones, DHEA and melatonin. Delta waves help suppress the production of cortisol, a hormone that is linked to stress and accelerated aging.
Stage 5
It's paradoxical sleep, it's dreams, that's where we classify and filter what we've seen and learned the day before. This is the reboot of his brain hard drive. This phase lasts between 10 and 20 minutes.
During REM sleep, the eyes move intensely under the eyelids, the neck becomes stiff, just like the sex of the man.
Remembering your dreams is a sign of good brain function: people who remember their dreams the best are often the most creative. In fact, dreaming is essential to the proper functioning of our brain.
The waves in relation to sleep in phase 5 are gamma waves, which circulate at the speed of 30 to 45 Hz per second. When the brain transmits a majority of gamma waves, brain and neural activity is at its peak, as during creative processes or complex problem solving.
What happens when you sleep badly?
Lack of sleep weakens the immune system, which accelerates oxidative stress and ultimately increases the rate of inflammation in the body. It brings about a degradation of the mood, an increase of the heart rate, a deterioration of the vision, a fall of the muscular force, a fall of the capacity of learning and concentration ... among others.
Some studies and figures in bulk ...
During sleep (during REM sleep more specifically, as mentioned above), the brain performs a reset of connections between neurons; these are often overloaded during the day and may limit our learning abilities. So, if you sleep badly, it's a safe bet that you will learn badly.
Sleeping 3 hours less than necessary for 3 days, endurance tests
Laissez un commentaireRépondre
Recherche sur le blog
Blog categories
